
#Roc curve in spss 20 code
This is necessary to ensure that the JavaScript code manipulates the correct svg elements. For documents that contain multiple interactive plots, it is necessary to assign each plot a unique name using the prefix argument of export_interactive_roc. In a knitr document, it is necessary to use the cat function on the results and use the chunk options results = 'asis' and fig.keep='none' so that the interactive plot is displayed correctly. The character string can be copy-pasted into an html document, or better yet, incorporated directly into a dynamic document using knitr ( knitr homepage).
The label and region stick until the next click.Īn interactive ROC plot can be exported by using the export_interactive_roc function, which returns a character string containing the necessary HTML and JavaScript. When the user clicks on the ROC curve, the confidence region for the TPF and FPF is overlaid using a grey rectangle. The confidence regions are automatically detected. Clicking makes the cutoff label stick until the next click, and if confidence regions are available, clicks will also display those as grey rectangles. Hovering over the display shows the cutoff value at the point nearest to the cursor. Furthermore, the points layer of the Roc geom can be hidden by using the hide.points option. This can be suppressed by add.cis = FALSE. By default, any existing Rocci layers are removed and replaced with a dense layer of confidence regions so that the user can click anywhere for a confidence region. Give the function an optional path to an html file as an argument called file to save the interactive plot as a complete web page. The style_roc function is applied by default.

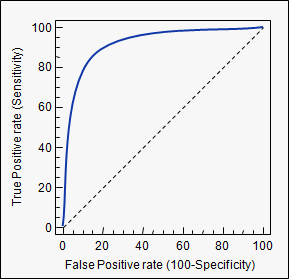
Ggplot objects that contain a GeomRoc layer can be used to create an interactive plot and display it in the Rstudio viewer or default web browser by passing it to the plot_interactive_roc, or export_interactive_roc function. This is exactly what the ROC curve is, \(FPF(c)\) on the \(x\) axis and \(TPF(c)\) along the \(y\) axis. Since the cutoff \(c\) is not usually fixed in advance, we can plot the TPF against the FPF for all possible values of \(c\). A bad outcome is when the test is positive among an individual who does not have the disease \(D = 0\).įormally, for a fixed cutoff \(c\), the true positive fraction is the probability of a test positive among the diseased population:Īnd the false positive fraction is the probability of a test positive among the healthy population:

In reference to the binary outcome that we denote as \(D\), a good outcome of the test is when the test is positive among an individual who truly has a disease: \(D = 1\). For a continuous measurement that we denote as \(M\), convention dictates that a test positive is defined as \(M\) exceeding some fixed threshold \(c\): \(M > c\). The accuracy of a diagnostic test can be evaluated by considering the two possible types of errors: false positives, and false negatives. ROC curves have also been used for a long time in signal detection theory. In medicine, ROC curves have a long history of use for evaluating diagnostic tests in radiology and general diagnostics. The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve is used to assess the accuracy of a continuous measurement for predicting a binary outcome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
